Written by: developervsandhu
Technology and Gadgets
Kotlin Control Statements
Control Statments
if
In Kotlin, if is an expression is which returns a value. It is used for control the flow of program structure. There is various type of if expression in Kotlin.
if(condation){
//code statement
}
// Syntax of traditional if else statement
if(condation){
//code statement
}
else{
//code statement
}
// Kotlin if-else Expression
val returnValue = if (condation) {
//code statement
} else {
// code statement
}
println(returnValue)
//
// Ladder if example
val grade: Char = if (marks in 91..100) {
'A'
} else if (marks in 81..90) {
'B'
} else if (marks in 71..80) {
'B'
} else {
'F'
}
When Expression
Kotlin, when expression is a conditional expression which returns the value. Kotlin, when expression is replacement of switch statement. Kotlin, when expression works as a switch statement of other language (Java, C++, C).
val grade: Char = when (marks) {
in 91..100 -> 'A'
in 81..90 -> 'B'
in 71..80 -> {
println("testing")
'C'
}
else -> {
'F'
}
}
println("Grade is $grade")
Programms
Loops
Repeat the statements n number of times
While
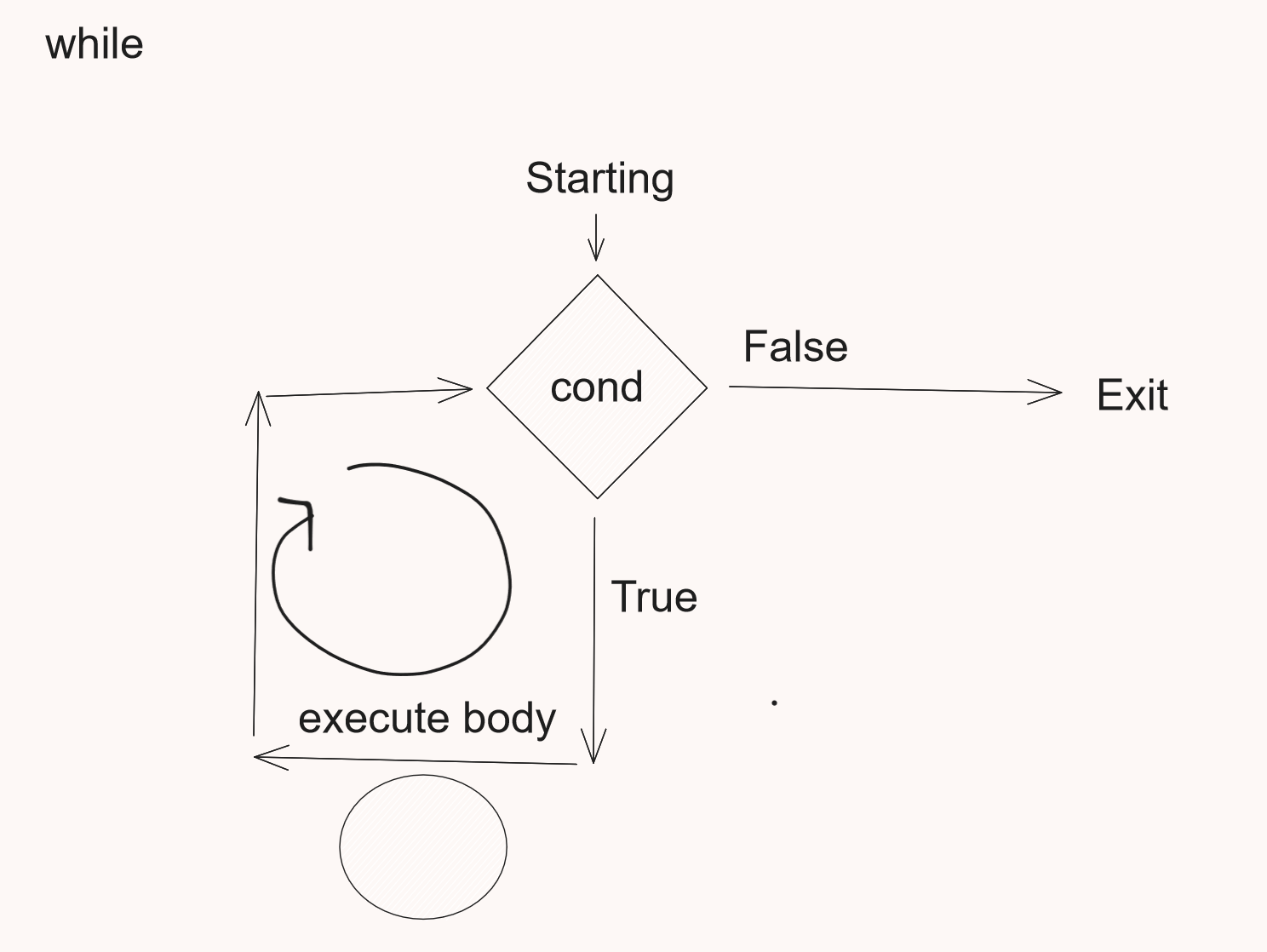
var count = 1
while (count <= 10)
{
// body statements
println("durgesh $count")
count++
}
println("Loop exited")
Do..While
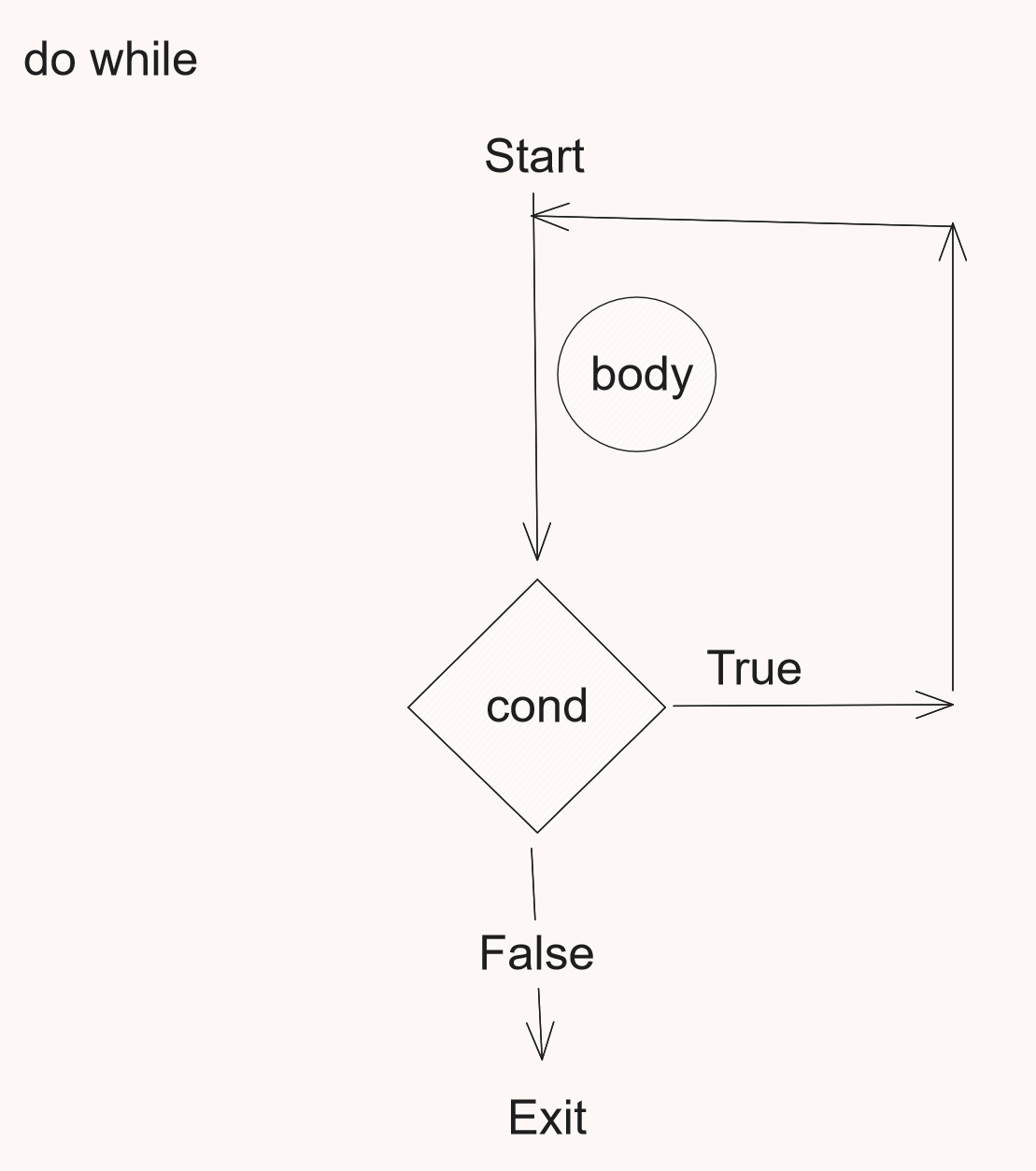
var count = 1
do {
println("durgesh $count")
count++
} while (count <= 10);
For loop
for (i in 10 downTo 1) {
println(i)
}
for (i in 0..100 step 3) {
println(i)
}
for (i in 1 ..9) {
println("i = $i")
}
val favActivities: Array<String> = arrayOf("cricket", "chess", "music", "programming")
for (activity in favActivities.reversed()) {
println(activity)
}
Watch First part
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1-LLZEGDOIc
Operators
Operators are the special symbols used to perform operations. eg +,-,>..
-
Arithmetic Operators
Perform methametical operations
| Operator | Example | Explanation | | -------- | ------- | ---------------- | | + | a+b | add two operands | | - | a-b | substract | | * | a*b | multiply | | / | a/b | Divide | | % | a%b | Modulus | | ++ | a++ | Increment | | -- | a-- | Decrement |
-
Assigment Operators
Assigns value to variable.
val a=5;
where = is assignment operator
We can use assignment and arthemetic operators togetter togetter the called Arithemetic Assignment Operators
| Operator | Example | Expansion | Explanation | | -------- | ------- | --------- | --------------------------------------- | | += | a+=b | a=a+b | Add a to b and then assign to a | | -= | a-=b | a=a-b | Substract b from a and then assign to a |
etc..
-
Comparison Operators
Compare two values
| Operator | Example | Explanation | | -------- | ------- | ------------------ | | == | a==b | Equal | | < | a<b | Less than | | > | a>b | Greater than | | <= | a<=b | Less than equal | | >= | a>=b | Greater than equal | | != | != | Not equal |
-
Logical Operators
Determain logic between to values
| Operator | Example | Explanation | | -------- | -------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- | | && | condition1 && condition2 | return true if both condition are true | | || | condition1 || condition2 | return true if any of two conditions are true | | ! | !a | reverse the result |
Hard Keywords
-
as
is used for type casts.
val ob: Any ="Testing" val test=ob as Stringspecifies an alias for an import
import java.util.ArrayList as SubstringList -
in
specifies the object being iterated in a for loop.
for(i in 1..10) { }is used as an infix operator to check that a value belongs to a range, a collection, or another entity that defines a 'contains' method.
if(i in collection) { }
is used in when expressions for the same purpose.
marks a type parameter as contravariant.
interface Demo<in T>
{
// T is only consumed never produced
}
-
is
checks that a value has a certain type.
is used in when expressions for the same purpose.
-
typealias
for type aliasing
typealias DkSet = Set<String>Do read : https://kotlinlang.org/docs/keyword-reference.html
Smart Typecasting( Smart Cast )
Kotlin convert types automatically if itcheck the type with is keyword in if condition.
fun test(value: Any) {
if (value is String) {
print(value.length)
} else {
print(value)
}
}
Functions in Kotlin
Set of statements written for doing a specific task.
Function has name, return type , parameters and modifiers.
how to define function in kotlin
fun keyword is used to defined function in kotlin
fun [functionName] ([parameter]) : [retunType]
{
//body of the function
return [Value]
}
//example
fun myFun(n1:Int, n2:Int):Int
{
return n1+n2
}
using the functions
Function can be used when we call the function
val result=myFun(2,5)
Default Argument
fun myFun(
b: ByteArray,
off: Int = 0,
len: Int = b.size,
) { /*...*/ }
Name argument
We can use name when calling
myFun(
off=4,
b=arr,
len=45
)
Lambda
Kotlin functions are the first class which means they can be stored in variables , passed as an argument , returned from another functions .
The function that takes another function as parameter or return another function is called Higher order functions.
fun highOrder(value: () -> Unit, intValue: Int): () -> Unit {
value()
return value
}
Varargs
Login To Add Comment
No comments yet.